ARTICLE AD BOX
Former president Joe Biden was diagnosed with an aggressive form of prostate cancer, a spokesperson for Biden announced on Sunday.
Biden, 82, is currently reviewing his treatment options with his family and physicians, the spokesperson added.
Last week, doctors found a “small nodule” on Biden’s prostate during a routine exam. After undergoing further testing, physicians determined it is prostate cancer with a Gleason score of 9 and has spread to the bone.
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer among men in the U.S., affecting approximately one in eight men during their lifetime.
While the condition is more likely to affect men over the age of 65, it can be diagnosed at a younger age.
From symptoms to treatment, here’s everything you need to know about the condition.

What is prostate cancer?
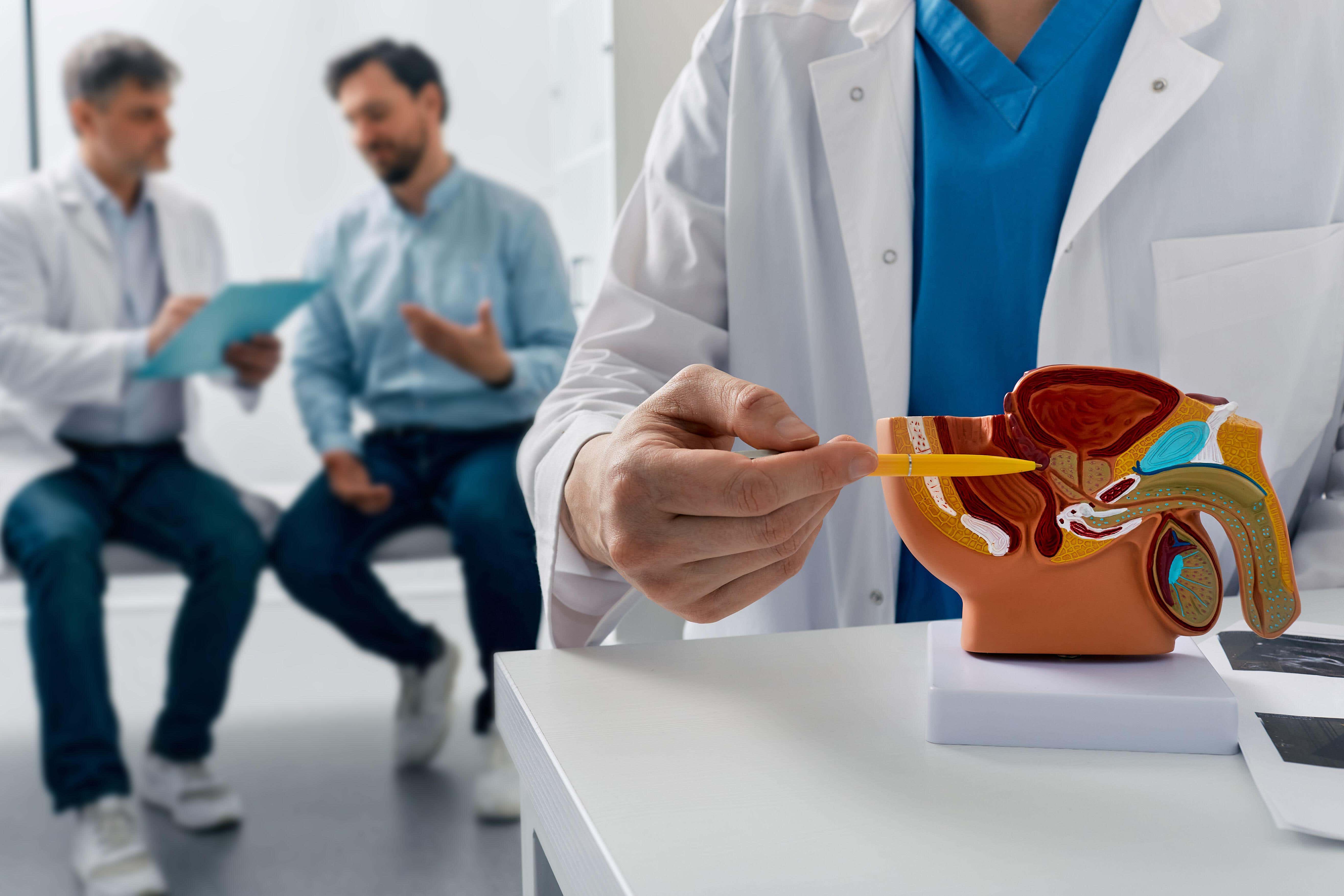
As the name suggests, prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland, which is located at the base of the bladder.
The main function of the prostate gland, a male reproductive organ, is to secrete prostate fluid, which mixes with sperm to create semen.
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut but enlarges as men age. It surrounds the first part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen.
When prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, this usually occurs in the outer gland cells of the prostate called acinar adenocarcinomas.
Cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin to divide and grow uncontrollably.
According to the American Cancer Association, the majority of cases of prostate cancer grow slowly and do not usually spread to other parts of the body.
When cancer has spread to another part of the body, it becomes known as metastatic cancer.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of prostate cancer may include frequent urination or problems urinating such as straining to urinate, feeling as though your bladder has not fully emptied, or seeing blood in urine or semen, the American Cancer Society says.
However, those systems are not always definitive indicators of prostate cancer. Older men may experience similar symptoms due to prostate enlargement, which is a non-cancerous condition.
Signs that prostate cancer has spread to other areas of the body may include back, hip or pelvis pain, erectile dysfunction, blood in urine or semen and unexplained weight loss, according to Mayo Clinic.
For more information about prostate cancer symptoms, you can visit the American Cancer Society or National Cancer Institute.
What are the causes?
While it is not known what causes prostate cancer, several factors may increase one’s risk of developing the condition.

Age is the most common risk factor for getting prostate cancer, according to the Center for Diseases Control.
Some people are at increased risk for getting prostate cancer including Black men or those who have a history of prostate cancer in their family.
Older men between the ages of 65 and 74 and non-Hispanic Black men are more likely to get prostate cancer.
How common is it?
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer among men in the United States.
The National Cancer Institute estimates that approximately 313,780 people will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2025. This represents around 15 percent of all new cancer diagnoses in the U.S.
In 2022, an estimated 3,518,978 men were living with prostate cancer.
How can it be treated?
There are several treatment options for people diagnosed with prostate cancer from just monitoring it to radiation therapy to surgery.
If a doctor believes the prostate cancer may not grow quickly, they can recommend active surveillance, which requires closely monitoring the cancer to see if it grows or causes symptoms, according to the CDC.
Some older men, often those not expected to live for 10 more years, can undergo “watchful waiting” which just consists of treating symptoms.
A person’s treatment may depend on whether their prostate cancer is localized in the prostate gland or has spread to other parts of the body.
Some people can undergo surgery, called a prostatectomy, which removes the prostate.

Hormone therapy, which blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones needed to grow, or radiation therapy, which kills cancer cells, can be used to treat prostate cancer.
In instances when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy or targeted therapy may be a treatment option.
If a person’s prostate cancer has become too advanced, then it may not be able to be cured.






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·