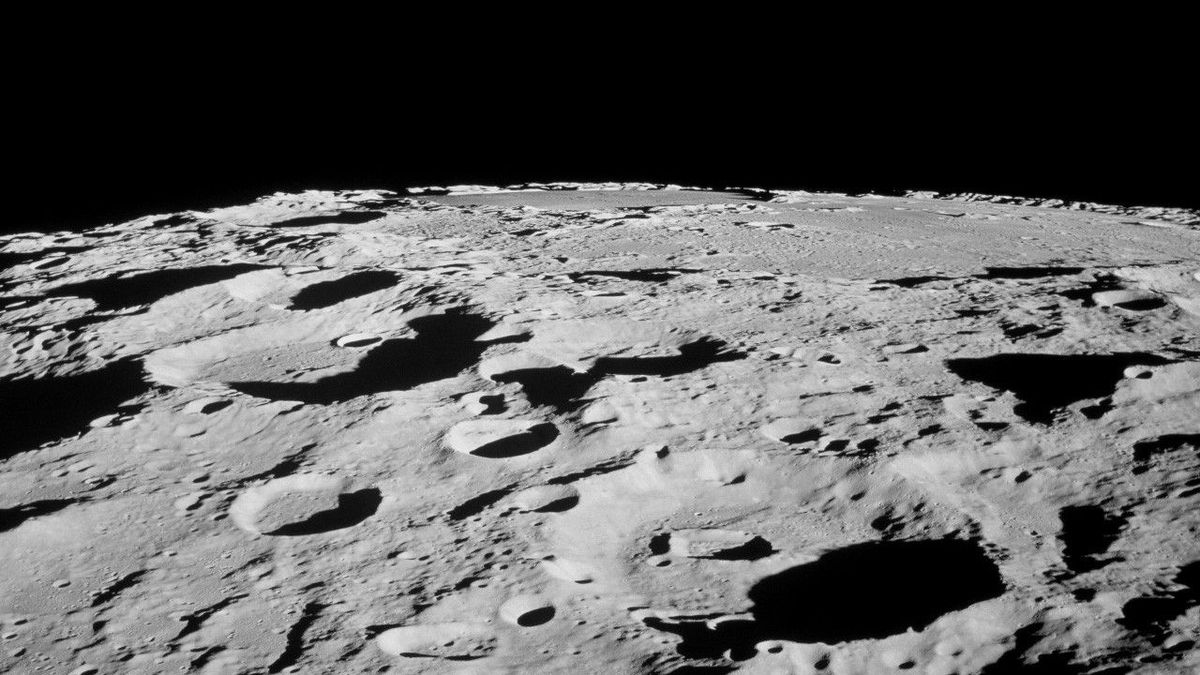
Precious moon samples brought back to Earth by China's Chang'e 5 mission in 2020 have finally been shared with international researchers — but the law has made it difficult for U.S.-based scientists to receive any of the material.
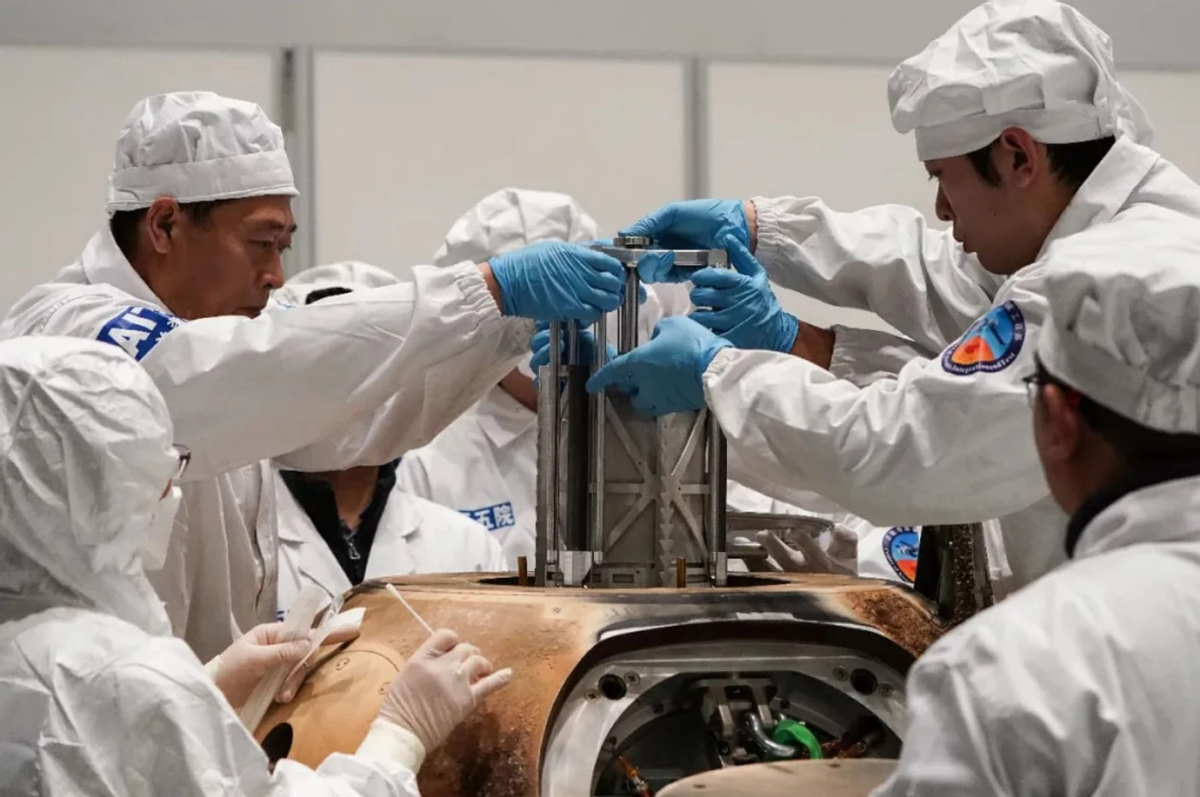
Earlier in May, British planetary scientist Mahesh Anand of the Open University in Milton Keynes travelled to China to "borrow" 60 milligrams (0.002 ounces) of the 1,731-gram (3.8 pounds) Chang'e 5 sample. Scientists from elsewhere in Europe, as well as Ethiopia, Russia and the United States, are also receiving samples.
In the other countries, government funding bodies are paying for the analysis of these loaned samples, but NASA is prevented from funding U.S.-based researchers to do the same. Instead, Timothy Glotch, the lone American planetary scientist who has received a sample of the Chang'e 5 material, had to be funded privately by his own institution, Stony Brook University in New York.
That's because of a law passed in 2011 called the Wolf Amendment. Named after Frank Wolf, the Republican senator who pushed for it, it was inserted as an amendment into the 2011 federal budget and bars bilateral cooperation between NASA (and the scientists the agency funds) and the China National Space Administration (CNSA) and Chinese scientists. The aim is to prevent Chinese government scientists from gaining knowledge of American space technologies that the U.S. government fears could then be used militarily by China against the United States.
The Wolf Amendment seems counter to the old way of doing things. Science has often been a bridge between opposing countries. During the Cold War, the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) was a project that U.S. and Soviet scientists worked together on, including a famous conference held in the USSR in 1971. Another example was the Apollo–Soyuz rendezvous in 1975, when astronauts and cosmonauts shook hands in space. The Wolf Amendment, however, prevents similar space-science cooperation taking place between the U.S. and Chinese governments without the prior approval of Congress.
And, it seems, the Wolf Amendment works both ways, preventing NASA from receiving or funding research into the Chinese moon samples.
Luckily for Glotch, this has not stopped China from sharing a sample with him and his research group, which includes scientists at San Francisco State University and the University of Hong Kong, as long as they are funded privately. Allowing American researchers access to the Chang'e 5 samples is important, because it allows them to make direct comparisons between Apollo-era lunar samples and the Chang'e 5 samples in the same lab.
Glotch plans to test the thermal properties of his "loaned" sample by heating it (we say loaned, but the analysis will likely destroy the sample), and then comparing it to thermal maps of the moon to provide a greater understanding of the composition of different lunar regions based on how they heat up and cool down in sunlight, relative to the Chang'e 5 sample.

The Chang'e 5 sample was obtained by the Chinese spacecraft from Mons Rümker, which is an ancient volcanic region in the giant Oceanus Procellarum ("Ocean of Storms"). By making direct comparisons between the Apollo samples, which were taken from various locations on the moon, and the Chang'e 5 sample, Glotch's group hopes to gain greater insights into the volcanism that created the samples in the first place.
Chinese scientists have already discovered that the basaltic material in the Chang'e 5 sample is substantially younger than the volcanic samples collected by Apollo, by billions of years. This tells us that the moon was volcanically active for much longer than scientists had realized — perhaps as recently as 120 million years ago.
Meanwhile, in the United Kingdom, Anand's team will heat some of their 60 milligram sample to 2,550 degrees Fahrenheit (1,400 degrees Celsius) to extract noble gases such as argon and krypton, as well as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, to provide more data about the history of those elements in the solar system.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·